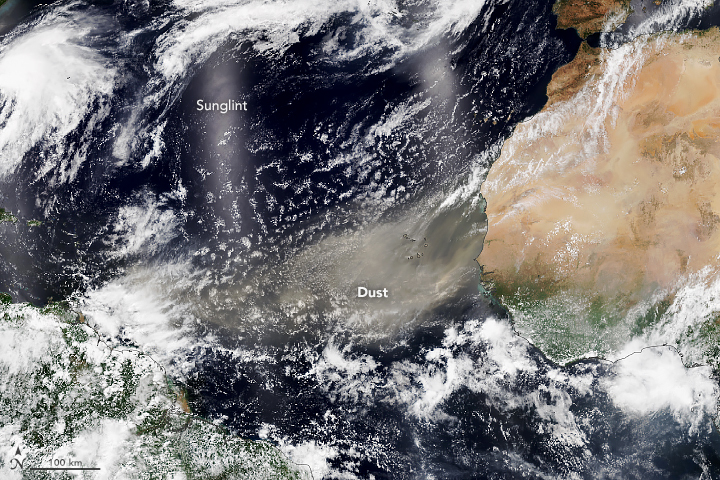
THE Saharan dust phenomenon, which has been increasing over the last few decades, has significant impacts on both human health and the environment.
Originating from the Sahara Desert in Africa, this dust is carried by winds across the Atlantic Ocean, affecting regions such as the Caribbean and the Americas.
For people with respiratory issues such as asthma or bronchitis, the increased dust can exacerbate their conditions, leading to breathing difficulties and other health problems. It can also cause irritation to the eyes, nose and throat, particularly in areas with high concentrations of dust.
However, Saharan dust can have positive effects as well. When it reaches the Amazon rainforest, thousands of miles away, it serves as a nutrient source for the trees. The minerals in the dust, such as phosphorus and iron, are essential for plant growth, particularly in nutrient-poor soils like those found in parts of the Amazon.
When next the Caribbean experiences a thick cloud of Saharan dust which could worsen air quality and impact those with respiratory issues, despite the negative effects on human health, it’s worth noting that this dust plays a vital role in the ecosystem, demonstrating the complex and interconnected nature of our planet’s systems.
Gordon Laughlin
Westmoorings


Responses